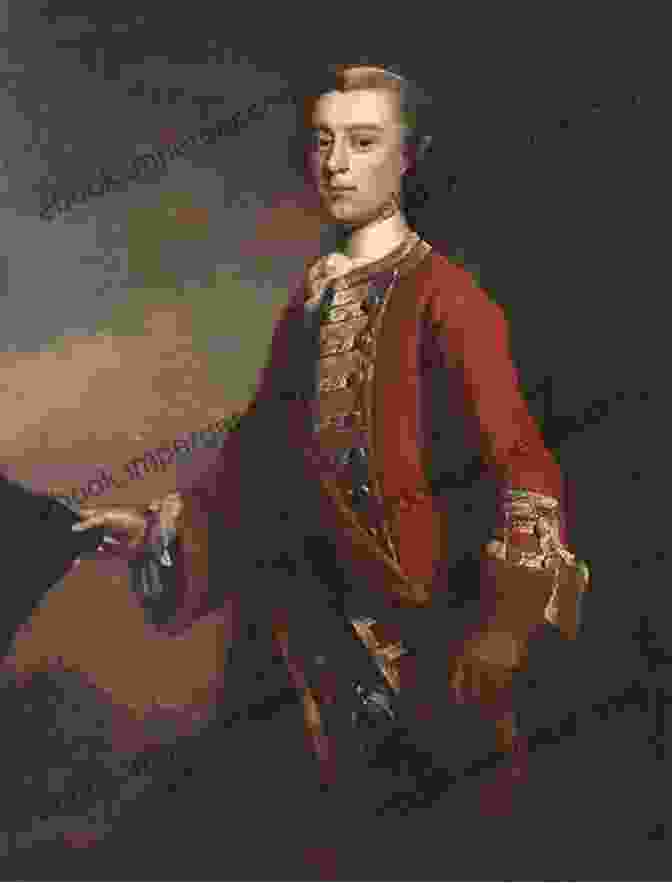
: The Prelude to a Defining Conflict
The year 1758 marked a pivotal juncture in the global power dynamics, as Britain and France engaged in a fierce struggle for supremacy in North America. Amidst this tumultuous era, a young and ambitious British general, James Wolfe, embarked on his first major campaign – the siege of Louisbourg. This audacious endeavor would not only test Wolfe's military prowess but also lay the foundation for his eventual triumph at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham.
The Strategic Importance of Louisbourg
Nestled on the southeastern coast of Cape Breton Island, Louisbourg was a formidable French fortress and a strategic gateway to the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Its capture would sever French supply lines to New France and pave the way for British control over Canada. Recognizing its immense significance, the British Admiralty assembled a formidable force under Wolfe's command to lay siege to this impregnable stronghold.
4.5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 51952 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 96 pages |

Wolfe's Bold Strategy
Undeterred by the formidable defenses of Louisbourg, Wolfe devised a daring plan. He aimed to land his troops at Freshwater Cove, a secluded spot three miles west of the fortress. From there, they would establish a camp and launch a relentless bombardment of the town's fortifications.
On June 8, 1758, Wolfe's fleet arrived off the coast of Louisbourg. Amidst rough seas and heavy fog, the British soldiers disembarked and marched towards their designated landing site. Despite fierce French resistance, Wolfe's troops successfully gained a foothold on the beachhead.
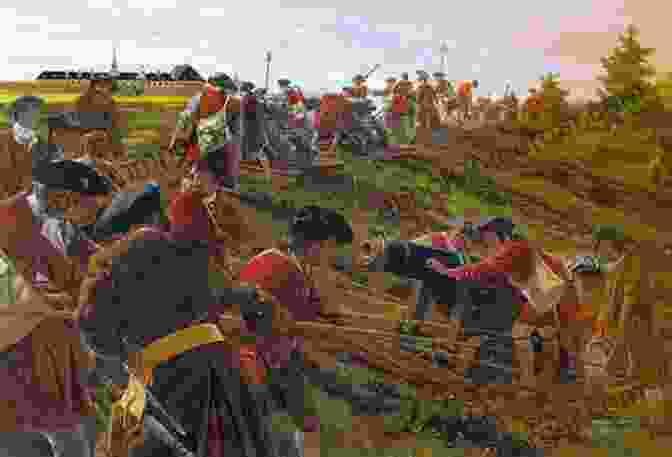

The Siege Unfolds: A Test of Endurance
With the beachhead secured, Wolfe's army set up camp and began to construct siege lines. They dug trenches, erected fortifications, and hauled heavy artillery pieces into position. The French garrison, under the command of Governor Augustin de Drucour, responded with equal determination, launching repeated sorties against the besiegers.
As the siege progressed, both sides endured unimaginable hardships. The British soldiers faced relentless artillery fire and disease, while the French garrison suffered from dwindling supplies and dwindling morale. The conflict became a bloody stalemate, with neither side able to gain a decisive advantage.
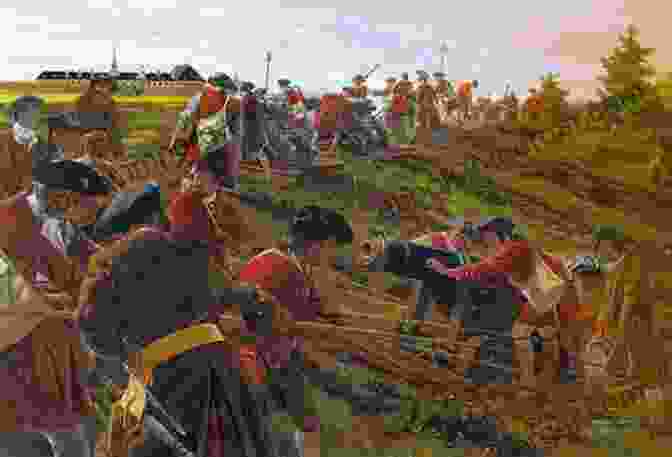

The Bombardment Intensifies: A Turning Point
On July 22, 1758, Wolfe Free Downloaded an all-out bombardment of Louisbourg's fortifications. For hours, the British artillery pounded the fortress, reducing its walls to rubble. The bombardment proved to be the turning point of the siege, as it shattered the French defenses and demoralized the garrison.
With their fortifications crumbling, the French had little choice but to surrender. On July 27, 1758, Governor Drucour hoisted the white flag, signaling the end of the siege. Louisbourg had fallen to the British.

Aftermath and Legacy: A Triumph for Wolfe
The capture of Louisbourg was a resounding victory for the British and a major setback for the French. It brought an end to the four-year French occupation of the island and paved the way for the eventual conquest of New France.
For Wolfe, the victory at Louisbourg proved to be a defining moment. It showcased his military brilliance, his determination, and his ability to inspire his troops. The success he achieved here propelled him to further glory at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham, where he would ultimately secure British supremacy in North America.

: A Pivotal Chapter in History
The siege of Louisbourg in 1758 stands as a testament to the courage, strategy, and endurance of the men involved. It was a pivotal chapter in the history of North America, marking the beginning of British dominance in the region and the eventual downfall of the French empire. Wolfe's victory at Louisbourg cemented his legacy as one of the greatest military commanders of his time and ensured his place in the annals of history.